A cervical herniated disc is diagnosed when the inner core of a disc in the neck herniates, or leaks out of the disc, and presses on an adjacent nerve root. It usually develops in the 30-to-50-year-old age group. While a cervical herniated disc may originate from some sort of trauma or neck injury, the symptoms commonly start spontaneously.
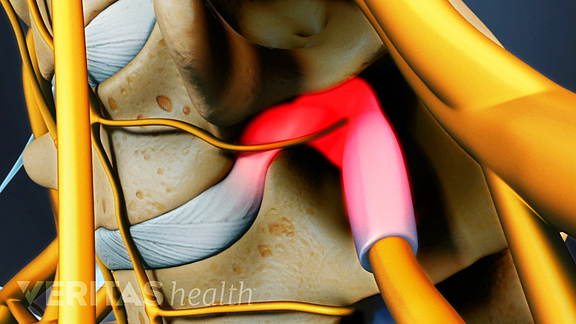
The arm pain from a cervical herniated disc results because the herniated disc material “pinches” or presses on a cervical nerve, causing pain to radiate along the nerve pathway down the arm. Along with the arm pain, numbness and tingling can be present down the arm and into the fingertips. Muscle weakness may also be present.
The discs in the cervical spine are not very large; however, there is also not a lot of space available for the nerves. This means that even a small cervical disc herniation may impinge on the nerve and cause significant pain. The arm pain is usually most severe as the nerve first becomes pinched.
Symptoms of a Cervical Herniated Disc
A cervical herniated disc can cause pain that radiates throughout the neck, shoulders, arms, and hands.
A herniated disc in the neck can cause a variety of symptoms in the neck, arm, hand, and fingers, as well as parts of the shoulder. The pain patterns and neurological deficits are largely determined by the location of the herniated disc.
See Cervical Spine Anatomy
The cervical spine is constructed around the vertebrae, or the 7 stacked bony building blocks in the spine. They are numbered top to bottom C1 through C7. The nerve that is affected by the cervical disc herniation is the one exiting the spine at that level, so at the C5-C6 level it is the C6 nerve root that is affected.
For example:
- C4-C5 (C5 nerve root): A herniation at this level can cause shoulder pain and weakness in the deltoid muscle at the top of the upper arm, and does not usually cause numbness or tingling.See All About the C2-C5 Spinal Motion Segments
- C5-C6 (C6 nerve root): A C5-C6 disc herniation can cause weakness in the biceps (muscles in the front of the upper arms) and wrist extensor muscles. Numbness and tingling along with pain can radiate to the thumb side of the hand. This is one of the most common levels for a cervical disc herniation to occur.See C5-C6 Treatment
- C6-C7 (C7 nerve root): A herniated disc in this area can cause weakness in the triceps (muscles in the back of the upper arm and extending to the forearm) and the finger extensor muscles. Numbness and tingling along with pain can radiate down the triceps and into the middle finger. This level is also one of the most common areas for a cervical disc herniation.See All About the C6-C7 Spinal Motion Segment
- C7-T1 (C8 nerve root): This level is located at the very bottom of the neck, where the cervical spine meets the thoracic, or upper, back. A herniation here can cause weakness with handgrip, along with numbness and tingling and pain that radiates down the arm to the little finger side of hand.
- See Understanding Hand Pain and Numbness
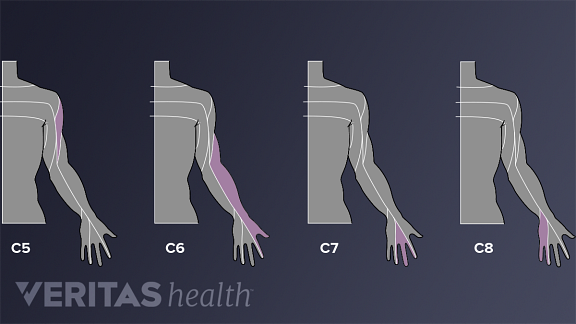
Typical pain areas for cervical disc herniation. Symptoms vary depending on which nerve root is compressed.
These are typical pain patterns associated with a cervical disc herniation, but they are not absolute. Some people are simply wired up differently than others, and therefore their arm pain and other symptoms will be different.